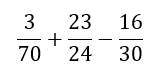First of all, we need to talk about the fractions.
A
fraction is a division between one number who’s going to be divided (dividend)
that we call here numerator, and the number who divides (divider) that we call
here denominator:
Then, how to do a sum between fractions?
You must have the same denominator if you want to sum the numerators. For this
purpose we must know how to do the least common multiple.
The least common
multiple is calculated when we have various denominators. We must calculate the
prime numbers that obtain a number when you multiply them.
A prime number is a number that can only be divided exatly by 1 and himself. For example 7 only can be divided by 1 and 7 so is a prime number. On the other hand 14 can be divided by 1,2,7 and 14 so it's not a prime number
A prime number is a number that can only be divided exatly by 1 and himself. For example 7 only can be divided by 1 and 7 so is a prime number. On the other hand 14 can be divided by 1,2,7 and 14 so it's not a prime number
For example the numbers 70, 24,30:
70 is even so it´s divisible between 2
and we obtain 35. 35 ends in 5 so it’s divisible between 5 and we obtain 7 that
it’s a prime number so that’s the last number we need to obtain. We can express
this in the next way:
Now that we have decomposed the numbers
in their prime numbers we can calculate the least common multiple by taking the
different numbers obtained at its maximum index, and multiply them:
Now we are going to use these numbers to
make fractions:
We have the least common
multiple of the denominators, the solution is obtained by multiplying the numerator and the
denominator by the same number until we obtain the least common multiple in the
denominator.
And now we can sum or differentiate them:
This is the basis of the fractional
calculus for sums and differences. The next post will be the castle of
fractions.