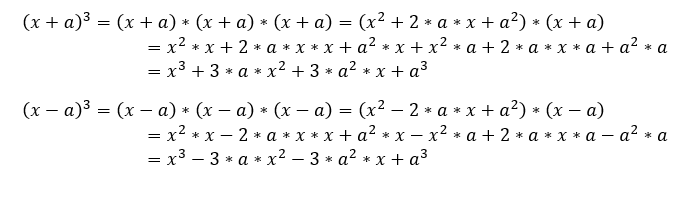A polinomial is a combination of variables. The variables must accomplish the equality to be called equation. When we are in 2D we only need one equation to obtain a curve.
An example of curve given by a polynomial would be:
Typically the variable “x” is called independent variable, and the “y” is called dependent variable because we give arbitrary values to the "x" and obtain values for "y". The variable “y” is written “y(x)” or f(x).
The operations sums and differences with polynomials must be made with variables raised to the same index. You can sum up the constants coefficients of that variables.
For example:
The degree of the polynomial would be the maximum value
between the indexs.
The degree shows you the amount of zeros of the problem. A
zero appears when y=0, this happens when the curve cross the “x” axis. So in
the previous graphic example we can find three zeros, one between -8 and -6, other
between -2 and 0 and the last one between 2 and 4.
To find the zeros of the polinomials there are analityc solutions (a formula to solve the problem exactly) until the degree 5; for bigger
degrees the analytic solution doesn’t exist.
The typical problem is to solve a polynomial of degree 2:
It has two possible solutions for "x":
Finally I’ll show how to do the product of a binomial, A binomial is a polynomial of two terms. The polynomials can be multiplied to obtain new polynomials. The product of a binomial is the easiest product between polynomials. The main products:
In particular:
And if we multiply once more: